The philosophy of lean manufacturing has gained prominence as one of the most manipulative production philosophies in the contemporary industrial world. Lean was developed out of the Toyota Production System (TPS), and it is aimed at creating maximum customer value with minimal waste. Running a small workshop, an enormous manufacturing facility, or an ever-changing industrial startup, Lean is a successful model to enhance efficiency, decrease expenditure, better the quality of the product, and reinforce competitiveness.
The following basic guide will cover the nature of lean manufacturing, its functioning, principles, tools, advantages, and the success of businesses in adopting the same.
What is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a method of manufacturing that enhances efficiency of production through waste reduction and streamlining production. Waste (called ‘muda’ in Japanese) is anything that is not contributing value to the end product, such as overproduction and flaws, as well as unnecessary movement and waiting.
Lean does not consist of a set of strict rules but rather a culture of continuous improvement. It gives employees authority, simplifies operations, and develops a flexible, responsive, and efficient production system.
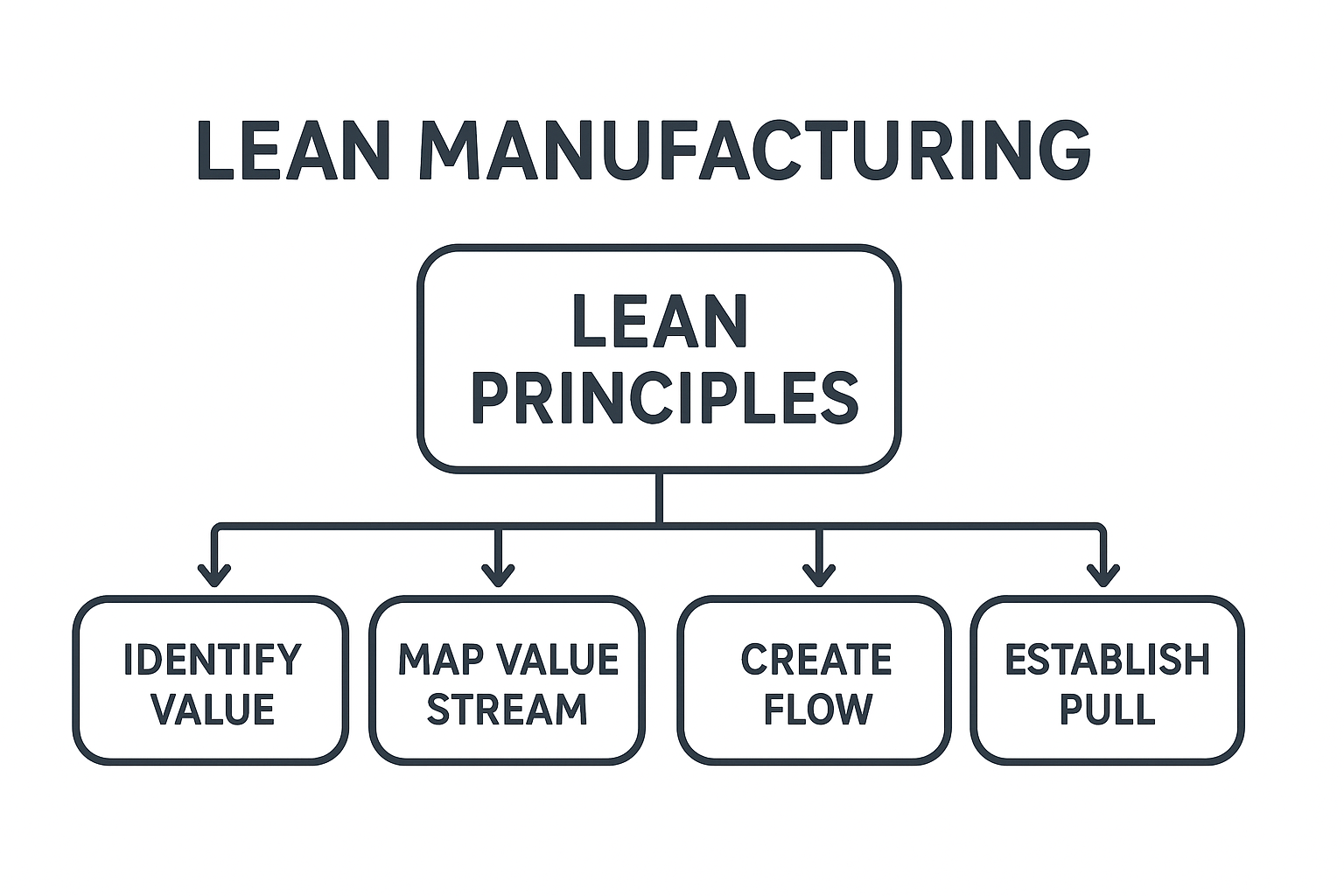
The 5 Principles of Lean Manufacturing.
Lean is founded on five principles that are acknowledged all over the world:
Identify Value
Value is the price that the customer is ready to pay. The initial process in the Lean is the perception of the customer expectations, quality requirements and pain points. All other things are waste.
Map the Value Stream
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) provides a map of all processes in the production process – from raw materials to delivery of products. This assists in determining those activities that add value and those that do not add value.
Create Flow
Once the waste is eliminated, the second thing to do is to make sure that there are no interruptions, delays and bottlenecks in production steps. Through a continuous flow, productivity is enhanced and lead time is decreased.
Establish Pull
Lean promotes a pull system instead of a push system, where the production of goods occurs only when the customer requires it, rather than ahead of demand. This is minimising the inventory and preventing overproduction.
Pursue Perfection
Lean is the process, rather than the place. In order to ensure efficiency and be competitive, there should be continuous improvement (Kaizen) so that processes can be refined.
Lean manufacturing wastes.
Seven wastes, or rather seven mudas, are identified by Lean:
Transportation – the movement of products that are not necessary.
Inventory – raw materials or completed products.
Motion – any unwarranted movement of workers or equipment.
Waiting – time is spent on procrastination.
Overproduction – manufacturing in excess.
Overprocessing – doing unnecessary work.
Quality defects – scrap or renew.
With the identification and removal of such wastes, business organisations are able to optimise manufacturing and save a lot of money.
The major lean manufacturing tools and techniques.
Lean applies some great tools in order to enhance the processes and to remove the waste. Others that have been extensively used are:
5S System
An organisational way in the workplace:
Sort
Set in Order
Shine
Standardise
Sustain
This provides a safe, efficient, clean working environment.
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
Minor incremental changes are done regularly. It promotes the involvement of employees and long-term optimisation.
Kanban
A legislative system that leads to a visual timetable, and this approach is a pull-based plan on production. Kanban is useful in the management of stocks and minimising excesses.
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Delivers the correct product, the correct quantity of it, at the correct moment. This reduces storage expenses and eliminates inventory.
Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing)
Creating methods of avoidance of errors prior to their happening. These may include colour-coded examples, a guide to the fixtures and sensor warnings.
Value Stream Mapping
A graphical illustration that could be used to recognise bottlenecks, redundancy and wastage in the production process.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Emphasisesequipment dependability and downtime reduction.
The advantages of lean manufacturing.
Introducing the concept of lean manufacturing can introduce radical changes to a company. Key benefits include:
Reduced Waste & Cost Savings
Businesses are able to reduce the number of materials used and enhance the efficiency of the usage of resources, as well as reduce the cost of doing business, by eliminating non-value-added activities.
Improved Productivity
Uncomplicated processes make workflow more rapid and effective in terms of labour and resources.
Better Product Quality
The lean tools such as Poka-Yoke and Kaizen minimise defects and maximise product consistency.
Shorter Lead Times
Continuous flow and pull systems save a lot of time in waiting and enable the manufacturers to react fast to the market requirements.
Higher Employee Morale
Lean promotes teamwork, problem-solving and ownership, resulting in a motivated workforce.
More Customer Satisfaction.
Swift delivery, quality assurance, and reduced prices have a direct positive effect on customer experience.
How to Exercise Lean Manufacturing in Your Business.
The move to Lean should be done in a strategic and methodological manner:
Begin with training & awareness.
Make sure that the employees are aware of Lean concepts and the intended goal of the change.
Carry out value stream mapping.
Examine the processes that you currently have to identify areas of inefficiency and waste.
Prioritise Areas of Improvement.
At the beginning, concentrate on such high-impact issues as bottlenecks, downtime, or overproduction.
Introduce Lean Tools
Begin with 5S, Kanban and Kaizen events so as to gain momentum.
Promote a Lean Culture
Promote dialogue, team empowerment, and recognition of the ongoing improvement.
Monitor, Measure & Adjust
Monitor progress by use of KPIs such as cycle time, defect rate and production efficiency.
Lean is not a one-time project. It involves continuous dedication and change.
Lean manufacturing in the contemporary world.
Lean manufacturing is now more significant in the era of automation, Industry 4.0, robotics, and smart factories. Although technology enables one to do more, Lean provides an efficient system that is smooth and economical.
Some of the industries that operate lean include:
Automotive
Aerospace
Electronics
Textiles
Pharma
Metal fabrication
Food processing
Heavy engineering
As the world gets increasingly competitive, Lean provides a long-term process of achieving optimal production coupled with enhancing customer value.
Conclusion
Lean manufacturing is not merely a cost-cutting philosophy, but it is a very holistic philosophy that changes the way business is conducted. Leveraging value, reduction of waste, empowering of teams and constant enhancement of processes, Lean helps organisations to expand, create and stay competitive.
Regardless of being a small producer or a huge industrial organisation, the adoption of Lean can result in the minimisation of expenditures, an increase in productivity, quality, and eventual success.